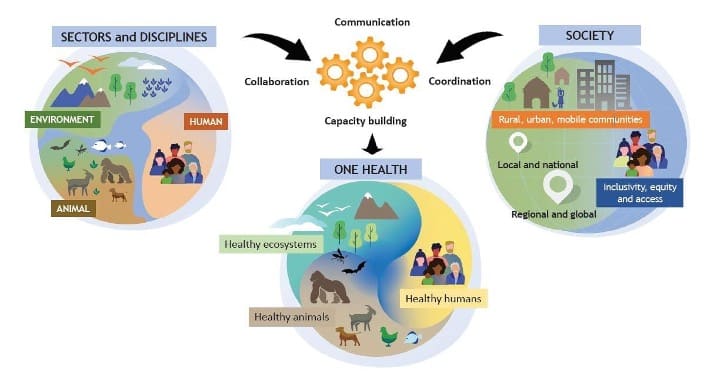
You cannot separate human health and the health of the planet: everything is connected. This is the principle of “one health”, in which a sustainable diet is absolutely fundamental. What we eat has consequences for the environment and for our own health. We need measures that take this broader context into account, tackling issues such as obesity without neglecting the pleasure of eating well.
Optimising human health invariably involves the health of animals, plants and the environment in general. This is the “one health” principle, which aims to sustainably balance and optimise the health of people, animals and ecosystems through an integrated, unifying approach. This approach also takes into account the needs of humans, particularly concerning nutritional requirements and resources, while at the same time taking measures in favour of the planet to contribute to sustainable development.
Also read: Our mission, achieving a sustainable change in eating behaviours
A tasty diet, good for people and the planet
We have to enjoy what we eat. It has to please our taste buds as well as our eyes, without forgetting that our choices have an impact not only on our health, but also on the environment, because the food chain has a carbon impact from start to finish. At every stage, we can limit that footprint: sensible and affordable choices can be made at the point of breeding and cultivation, during transport and sale, right up to the point of preparation and eating a meal that is both delicious and beneficial. These choices can be good for the environment, while considering human needs and, above all, the joy of good food. You’ll see, it’s both easy and delicious!
From this perspective, a sustainable diet takes into account the needs of both humans and the planet. As stated in its definition, it has to take into account several factors:
“Sustainable diets are those diets with low environmental impacts which contribute to food and nutrition security and to healthy life for present and future generations.”
FAO, 2010, Sustainable Diets and Biodiversity.
Eating sustainably is also a key factor in tackling chronic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. The ‘one health’ principle promotes a holistic approach to combatting these diseases.
Also read: Combatting obesity boosts economic and social well-being
Obesity affects all ecosystems
Obesity is an ever-growing global challenge. By 2030, more than one in five women and one in seven men will be obese, according to the latest global obesity report. To combat this problem over the long term, it’s not enough to target the disease alone. We need an approach that also takes into account undernutrition and climate change. We need to see the disease in a wider context, in which prevention is as important as treatment, while taking into account climate issues.
Our diet and our food system, standing at the heart of this discussion, must evolve to promote a diet which is healthy and nutritious while also sustainable.
You may also be interested: How to help citizens in need while fighting against food waste



 Eggplant
Eggplant  Bean sprouts
Bean sprouts  Vegetable garden: growing rocket
Vegetable garden: growing rocket 









